Projects
The purpose of the investment project BTH-NIB is the assurance of the appropriate infrastructural conditions for the use of research and developmental opportunities in the fields of operation of the NIB.
Play Video About project Publication
Structure and function of ecosystems
Project coordinator: David Stanković, PhD
Code: P1-0255
Duration: 1. 1. 2017 - 31. 21. 2027
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the Slovenian Research Agency (research core funding No. P1-0255).
Abstract
To understand the fundamental mechanisms underlying the structure and function of natural and anthropogenic ecosystems, it is necessary to gain insight into the patterns of their biological diversity and the underlying processes that generate them. In the Anthropocene, the health and resilience of ecosystems are being rapidly altered by human activity. Consequently, we are facing ecosystem collapse and a biodiversity crisis with unforeseen consequences for human society. The long-running research program Structure and Function of Ecosystems addresses key scientific questions and issues that are central to sustainable development and the protection of biodiversity for future generations.
The programme is implemented by the Department of Organisms and Ecosystems Research at the National Institute of Biology (EKOS-NIB) and by the Slovenian Museum of Natural History (PMSL). The program is led by NIB, and for EKOS it is the only source of long-term, stable financial support that enables us to conduct integrative, long-term field studies, which are crucial in ecosystem research. The PMSL archives historical zoological collections and records that are invaluable in unravelling effects of human activity on biodiversity and can serve as a basic infrastructure for setting conservation targets. Its inclusion in our research program enables it to fulfil its role in accordance with the ICOM Code of Ethics for Natural History Museums in conducting research and supporting the science and biological conservation.
Overrarching goals: (I) to reveal the key evolutionary and ecological mechanisms underlying biodiversity patterns and (II) to define measures for effective biodiversity conservation along with sustainable use of natural resources.
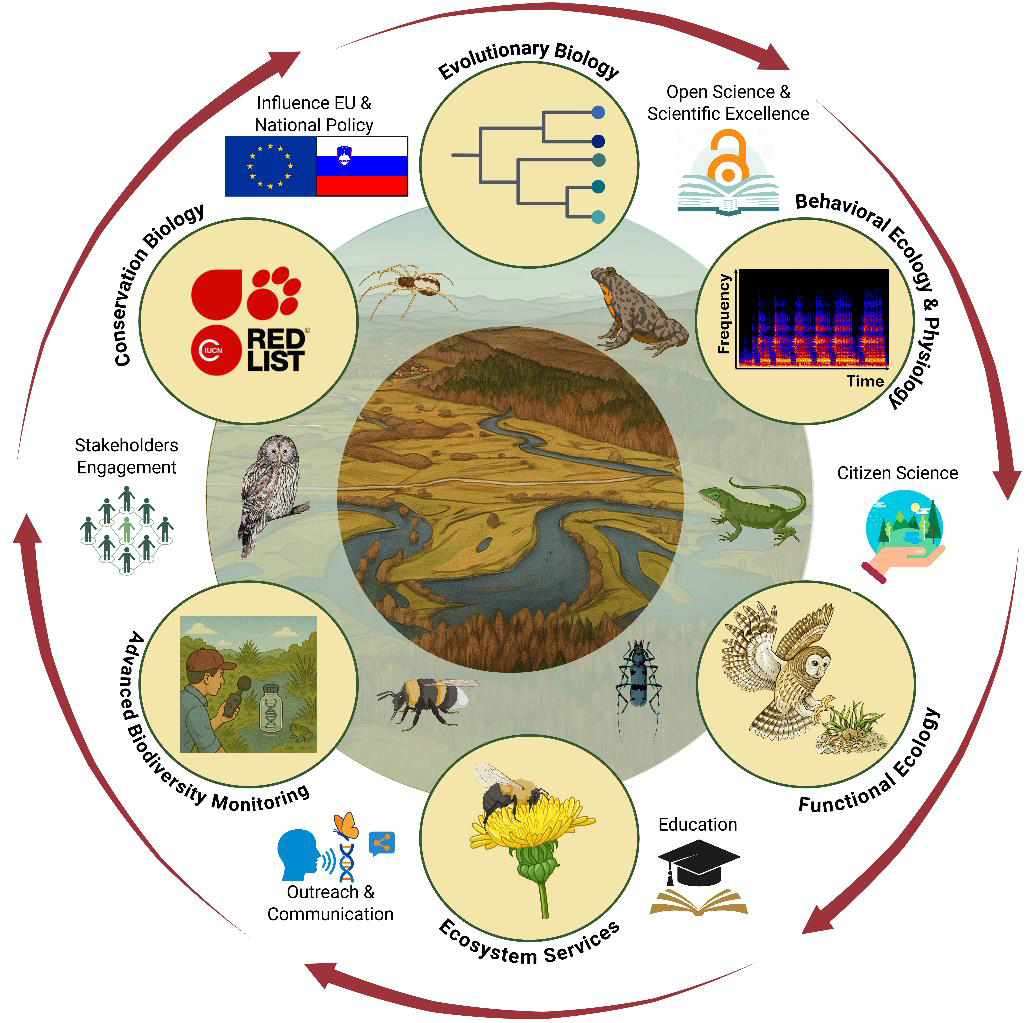
Structure of the research program “Structure and Function of Ecosystems”. The interdisciplinary research at EKOS focuses on six complementary areas (Evolutionary Biology, Behavioral Ecology & Physiology, Functional Ecology, Ecosystem Services, Advanced Biodiversity Monitoring, Conservation Biology). The program also supports scientific excellence, citizen science, knowledge transfer, engagement with stakeholders and policy makers, and the promotion of science.
Expected impact of the research program
The outcomes of this program will have positive long-term impacts, either by opening up new areas of research or by enabling more efficient nature conservation and management policies. First and foremost, they will provide much needed empirical data for the development of novel and advanced approaches for the conservation of ecosystem services and the control of invasive species, as well as for the development of innovative protection measures and conservation management strategies. This is crucial for efficient biodiversity conservation that ensures healthy ecosystems and human well-being in Slovenia and globally.
The expected results of this program are firmly anchored in the three pillars of sustainable development (economic and social development, and environmental protection). Our research supports the national and international strategic goals of the Strategy of NIB, the Strategy of Development of the Republic of Slovenia 2030, the Biodiversity Conservation Strategy of Slovenia, the UN 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, the UN post-2020 Global Biodiversity Framework, EU ‘One Health’ policy, EU Common Agricultural Policy, EU ‘Farm to Fork’ strategy, the EU Water Framework directive, the EU Green Deal, the EU Biodiversity Strategy 2030, the EU Birds Directive and the EU Habitats Directive.
Denial of biodiversity and climate crises has been identified as one of the most important global conservation issues. Through citizen science and our numerous outreach and educational activities, we raise awareness among the general public, students, professionals and policy makers about the importance of biodiversity and nature conservation for the well-being of society.
Information about the programme (SICRIS)


 Scope of NIB's accreditation is given in the Annex to the accreditation certificate and in the List of accredited methods for detection of GMOs and microorganisms – plant pathogens
Scope of NIB's accreditation is given in the Annex to the accreditation certificate and in the List of accredited methods for detection of GMOs and microorganisms – plant pathogens 
