Oprema v laboratoriju
Microbial ecology

MICROBIAL ECOLOGY
![]()
WHO WE ARE
Head of researh group:
Assoc. Prof. dr. Valentina Turk
Post Doctoral researcher:
PhD students:
Master students:
Ana Fortič
Previous PhD students:
Dr. Jana Vojvoda
Oceans and seas represent the largest part of the Earth’s biosphere and marine microbes are the most abundant group of organisms, capable of growing in all marine habitats. Microbes are the key players in marine food webs and are involved in all biogeochemical cycles. The central focus of our research is to study the impacts of variable supply regimes of different inorganic and organic matter on the function and diversity of the microbial communities, mainly Bacteria and Achaea, in shallow enclosed coastal marine ecosystems. Oceanographic properties are strongly affected by water mass exchange, river inflow and meteorological conditions, which influence the microbial community composition and function.
Our recent and ongoing projects are especially focusing on the microbial community response to changes of physiochemical environmental parameters, phytoplankton blooms, massive gelatinous zooplankton outbreaks and accumulations of organic matter (i.e. marine snow, macroaggregates).Furthermore, we are investigating the response of marine microbial communities to different source of anthropogenic pollutants.

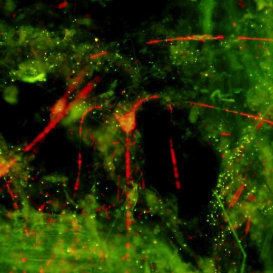
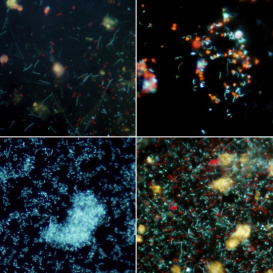
FIELD OF RESEARCH

MOST IMPORTANT ARTICLES
- Tinta T, J Vojvoda, P Mozetič, I Talaber, M Vodopivec, F Malfatti, V Turk. 2014. Bacterial community shift is induced by dynamic environmental parameters in a changing coastal ecosystem (northern Adriatic, NE Mediterranean Sea) - a 2 year time series study. Environmental microbiology, doi:10.1111/1462-2920.12519. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/1462-2920.12519/abstract;jsessionid=67C0A7EA14C461019144A63D24F58EEA.f03t02
- Malfatti F, V Turk, T Tinta, P Mozetič, M Manganelli, S J Samo, J A Ugalde, N Kovač, M Stefanelli, M Antonioli, S Fonda Umani, P Del Negro, B Cataletto, A Hozić, D Ivošević N Žutić, V Svetličić, T Mišić Radić, T Radić, D Fuks, F Azam. 2014. Microbial mechanisms coupling carbon and phosphorus cycles in phosphorous-limited northern Adriatic Sea. Science of the total environment, doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.10.040.http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969713011844
- Carvalho R N, A Aruqwe, S Ait-Aissa, A Bado-Nilles, S Balzamo, A Baun, S Belkin, L Blaha, F Brion, D Conti, V Flander Putrle, V Turk, et al. 2014. Mixtures of Chemical Pollutants at European Legislation Safety Concentrations: How Safe are They?. Toxicological sciences. an official journal of the Society of Toxicology, doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfu118 http://toxsci.oxfordjournals.org/content/early/2014/06/23/toxsci.kfu118.abstract?sid=d8381fd4-bf03-4904-92c7-b67ce34bb084
- Mikaelyan SA, A Malej, T Shiganova, V Turk, A E Sivkovitch, E I Musaeva, T Kogovšek, T A Lukasheva. 2014. Populations of the red tide forming dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans (Macartney): a comparison between the Black Sea and the northern Adriatic sea. Harmful algae, 33: 29-40. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2014.01.004
- Sjöstedt J, M Pontarp, T Tinta, H Alfredsson, V Turk, P Lundberg, Å Hagström, L Riemann. 2013. Reduced diversity and changed bacterioplankton community composition do not affect utilisation of dissolved organic matter in the Adriatic Sea. Aquatic microbial ecology, 71: 15-24, doi: 10.3354/ame01660 http://www.int-res.com/prepress/a01660.html
- Tinta T, T Kogovšek, A Malej, V Turk. 2012. Jellyfish modulate bacterial dynamic and community structure. PloS one, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039274. http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0039274,
- Cozzi S, C Falconi, C Cornici, B Čermelj B, N Kovač, V Turk, M Giani. 2012. Recent evolution of river discharges in the Gulf of Trieste and their potential response to climate changes and anthropogenic pressure. Estuarine, coastal and shelf science, 115: 14-24, doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2012.03.005
- Turk V, Å Hagström, N Kovač, J Faganeli. 2010. Composition and function of mucilage macroaggregates in the northern Adriatic. V: SAME 11 - The 11th Symposium on Aquatic Microbial Ecology, August 30 - September 04 2009, Piran, Slovenia. DEL GIORGIO, Paul A. (ur.). Progress and perspectives in aquatic microbial ecology, Aquatic microbial ecology, 61, 279-289, doi: 10.3354/ame01447
- Tang K W, V Turk, H P Grossart. 2010. Linkage between crustacean zooplankton and aquatic bacteria. In: SAME 11 - The 11th Symposium on Aquatic Microbial Ecology, August 30 - September 04 2009, Piran, Slovenia. DEL GIORGIO, Paul A. (ur.). Progress and perspectives in aquatic microbial ecology, Aquatic microbial ecology, 61, 261-277, doi: 10.3354/ame01424.
- Tinta T, Malej A, M Kos Kramar, V Turk. 2010. Degradation of the Adriatic medusa Aurelia sp. by ambient bacteria. Hydrobiologia. doi: 10.1007/s10750-010-0223-x. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0223-x,
- Turk V, D Lučić, V Flander Putrle, A Malej. 2008. Feeding of Aurelia sp. (Scyphozoa) and links to the microbial foodweb. Marine ecology, 29: 495-505
- Malej A, V Turk, D Lučić, A Benović. 2007. Diel vertical migration and the trophic interactions of moon jelly (Aurelia sp.) Mar. biol. (Berl.), 3,151, 827-841 JCR IF (2007) 2.215.
- Turk V, T Tinta, N Galavš, O Bajt, N Kovač. 2013. Degradation of bioplastic in marine environment. Rapports et Proces Verbaux des Réunions - Commission Internationale pour l'Exploration Scientifique de la Mer Méditerranée, ISSN 0373-434X, Vol 40: 312. http://www.ciesm.org/online/archives/abstracts/pdf/40/index.php.
PHOTOGALLERY

 NIB - MORSKA BIOLOŠKA POSTAJA PIRAN
NIB - MORSKA BIOLOŠKA POSTAJA PIRAN